Describe an Alternate Pathway Within the Rock Cycle
Sedimentary rocks are formed from pieces of other existing rock or organic material. The rock cycle is a series of processes in which water wind or waves break up rocks.
Alternate Pathways Rock can follow many different pathways through the rock cycle.
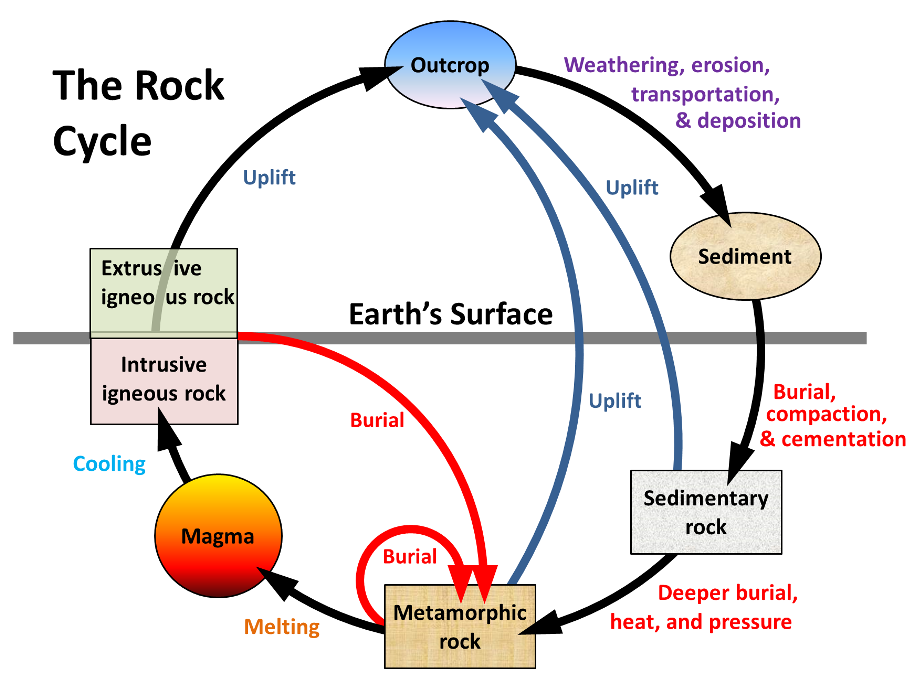
. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changessuch as melting cooling eroding compacting or deformingthat are part of the rock cycle. The concept of uniformitarianism which says that the same Earth processes at work today have occurred throughout geologic time helped develop the idea of the rock cycle in the 1700s. Describe an alternate pathway within the rock cycle.
The key processes of the rock cycle are crystallization erosion and sedimentation and metamorphism. The rock cycle is driven by two forces. If the conditions no longer exist for the magma to stay in its liquid state it will solidify into an igneous rock.
Be as detailed as possible and think carefully about this. We learned the difference between extrusive and intrusive igneous rock. One starts at igneous rock and when heat and pressure are applied it turns into metamorphic rockanother is a.
An example of and intrusive igneous rock may be referred to as a pluton or. Magma cools either underground or on the surface and hardens into an igneous rock. The rock cycle describes the processes through which the three main rock types igneous metamorphic and sedimentary transform from one type into another.
Describe an alternate pathway within the rock cycle. Pathway 1 Between New Zealand and South America at the bottom of the Pacific Ocean molten material from the mantle erupts from the mid-ocean ridge. The rock cycle is a process in which pressure causes sediment particles to cement together.
Rocks of any type can be converted into any other type or into another rock of the same type as this diagram illustrates. Igneous sedimentary and metamorphicThe cycle outlines how each rock type can be converted to another rock type through geologic processes. 31 The Rock Cycle The rock components of the crust are slowly but constantly being changed from one form to another and the processes involved are summarized in the rock cycle Figure 32.
The rock cycle is a process in which heated magma cools to form igneous rock. The key processes of the rock cycle are crystallization erosion and sedimentation and metamorphism. Remember there are different pathways.
Processes in the rock cycle occur at many different rates. What is an alternate pathway in the rock cycle. 1 Earths internal heat engine which moves material around in the core and the mantle and leads to slow but significant changes within the crust.
Most of us think of rocks as objects which dont change. As the material comes into contact with the very cold ocean water it cools. The rock cycle is the set of processes by which Earth materials change from one form to another over time.
Here are two examples. Rocks at the surface are lying in place before they are next exposed to a process that will change them. Sedimentary metamorphic and igneousEach rock type is altered when it is forced out of its equilibrium conditions.
When rocks are pushed deep under the earths surface they may melt into magma. Rocks are broadly classified into three groups. For example an igneous rock such as basalt may break down and dissolve when exposed to the atmosphere or melt as it is.
Several processes can turn one type of rock into another type of rock. The rock cycle is a basic concept in geology that describes transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types. Rock Cycle Diagram.
Plate movements drive the rocks cycle by pushing rocks back into the mantle where they melt and become magma again. This indicates how strong in your memory this concept is. Describe the process of how an igneous rock can transform into a sedimentary rock.
There are three main types of rocks. The formation movement and transformation of rocks results from Earths internal heat pressure from tectonic processes and the effects of water wind gravity and biological including human activities. Describe at least two different possible scenarios of the rock cycle.
Rocks deep within the Earth are right now becoming other types of rocks. Processes of the Rock Cycle. What is the rock cycle.
By building destroying and changing rocks in the crust. Presents the three major rock types and the processes that lead to their formation in the rock cycle. An alternative pathway in the rock cycle suggests that rocks might transform in various ways based on different scenarios associated with weathering.
The rock cycle is a concept of geology that describes the transition of rocks between the three rock types. Loose particles created by the weathering and erosion of rock by chemical precipitation from solutions in water or from the secretions of organisms and transported by water winds or glaciers. Analogous to recycling a Coke can where an old.
The Rock Cycle. The rock cycle is a series of processes in which one kind of rock is transformed into. Several processes can turn one type of rock into another type of rock.
Igneous sedimentary and metamorphic and the simplest diagram of the rock cycle puts these three groups in a circle with arrows pointing from igneous to sedimentary from sedimentary to metamorphic and from metamorphic to igneous again. Practice Rock Cycle Processes. What do plate movement cause that drives rocks through the rock cycle.
The Rock Cycle is Earths great recycling process where igneous metamorphic and sedimentary rocks can all be derived from and form one another. The rock cycle is a process in which rocks are continuously transformed between the three rock types igneous sedimentary and metamorphic. Sedimentary igneous and metamorphic.
Conversion to metamorphic rocks requires conditions of increased temperature andor increased pressure.


Comments
Post a Comment